Rudi Reinhardt, M.Sc.
Doctoral Candidate
Building: 31 (Physik Ost)
Room: 01.007
E-mail: rudi.reinhardt@uni-wuerzburg.de
Since 01/12/2025:
PhD candidate at the Institute for Theoretical Physics and Astrophysics / Chair of Astronomy of the Julius-Maximilians-University, Würzburg, Germany
Supervisor: Dr. Thomas Siegert
01/04/2023 – 02/10/2025:
Physics studies (M.Sc.) at Julius-Maximilians-University, Würzburg, Germany
01/10/2018 – 20/06/2023:
Physics studies (B.Sc.) at Julius-Maximilians-University, Würzburg, Germany
26/06/2015:
Abitur, Hennebergische Gymnasium "Georg Ernst", Schleusingen, Germany
12/07/1996:
Born in Suhl, Germany
Time-variabilities in the Galactic Positron Annihilation Signal
The interaction of low-energy cosmic-rays (CRs) with various asteroid populations in our Solar System might contribute significantly to the measured Galactic gamma-ray emission. The contribution of this time-variable signal is particularly strong for the 511 keV positron annihilation line and can reach up to 20%, according to previous studies, depending on the asteroid population, its properties, and its motion with respect to Earth. In a 20 yr INTEGRAL/SPI dataset, we explicitly search for this Solar System gamma-ray foreground emission.
In a second step, we provide more accurate flux estimates of the signals from all asteroid populations within the Milky Way in the MeV range using simulations based on the GEANT4 framework.
Scintillation detector-based Localization and Characterization of Radioactive Material (scintLaCHARM)
Together with partners from Hellma Materials, Brenk Systemplanung, the Fraunhofer Institute for Scientific and Technical Trend Analysis (INT), and Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz, we are planning to use scintillation-based Compton cameras and spectrometers for the decommissioning of nuclear power plants. The goal is to engineere satellite-grade technology into cameras capable of mapping contamination within nuclear facilities. The software will be based on the cosipy framework developed for the Compton Spectrometer and Imager (COSI).
The project is funded by the BMFTR (Bundesministerium für Forschung, Technologie und Raumfahrt) as part of the FORKA (Forschung für den Rückbau kerntechnischer Anlagen) funding program under the reference number: 15S9455 A-E.
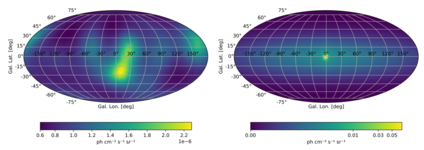
Goal: Estimation of the gamma-ray flux and morphology from annihilating positrons inside and in the walls of the Local Bubble.
Methods: Spatial modelling, line-of-sight integration (discrete and Monte Carlo), differential equations, diffusion, data simulations (COSI SMEX).
Link to Bachelor thesis: Link